Policy options for promoting high-speed broadband
It is now widely recognised that broadband is an essential pillar of a successful economy, and that the widespread availability and use of broadband has both economic and social benefits. As economies become increasingly reliant on digital networks, governments are now looking to promote next-generation broadband networks.
Governments are implementing national broadband plans that define specific goals and the different policy instruments required to reach those goals. The objectives set out in these plans typically address two areas: supply (e.g. coverage of networks) and demand (e.g. take-up and usage of services).
In most countries, reaching ubiquitous or near-ubiquitous coverage of high-speed broadband is likely to require public funding, as the high costs of rolling out broadband infrastructure reduce the economic viability of high-speed broadband in low-density areas.
Besides public funding, various policy options have been identified by governments, which can be classified as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Main types of policy to promote the demand for and supply of broadband networks [Source: Analysys Mason, 2015]
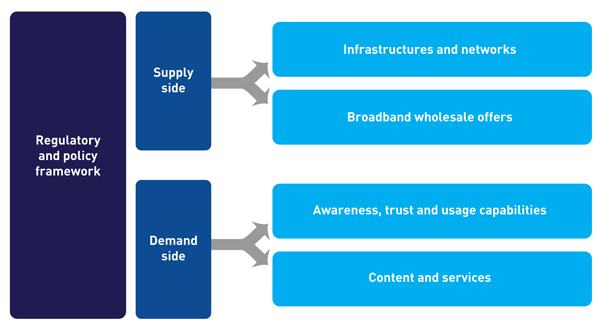
Figure 2 presents examples of supply-side measures that can be taken to promote the supply of broadband networks and services, and high-speed broadband in particular.
Figure 2: Supply-side measures to promote provision of broadband networks and services [Source: Analysys Mason, 2015]
| Type of policy | Definition |
| Sharing of telecoms infrastructure | Adopt measures to promote the sharing of existing telecoms infrastructure among players that would benefit operators through a reduction in roll-out costs |
| Co-deployment and co-investment | Introduce measures to enable co-ordination and joint investment in the roll-out of communications networks by telecoms operators, possibly in conjunction with utilities/promoters |
| Access to non-telecoms infrastructure | Introduce measures to allow operators to use non-telecoms civil infrastructure when deploying communications networks |
| Spectrum assignment | Take action to define a clear and efficient spectrum policy to encourage the development of mobile broadband |
| Spectrum trading | Introduce the option to transfer spectrum rights, to improve flexibility in the use of frequencies |
| Coverage obligations | Design new spectrum licences in a way which will increase the availability of broadband networks and services at a national level |
| Imposition of technical standards | Eliminate uncertainty regarding the technical specifications for broadband roll-out projects |
| Wholesale and retail markets | Introduce measures to promote competition to allow potential new operators to successfully enter the market |
Figure 3 outlines examples of measures that can be implemented on the demand side, to facilitate the use of broadband by the largest number of citizens possible and increase the amount and attractiveness of digital content and services in order to foster citizens’ interest in ICT.
Figure 3: Demand-side measures [Source: Analysys Mason, 2015]
| Type of policy | Definition |
| Broadband mapping | Develop a publicly accessible mapping tool to display the availability and speed of retail broadband connections, on a nationwide basis |
| Transparency and control | Set up transparency requirements for operators to enhance information, control and trust for end users in relation to broadband |
| Communication | Design marketing campaigns to encourage the widespread use of digital services |
| Trust and security | Introduce measures to improve security for users of digital services and increase their confidence in these technologies |
| e Inclusion and ICT literacy | Implement measures to foster access to, and use of, ICT content and services by the vast majority of the population |
| e-Education e-Administration e-Health e-Commerce e-Justice |
Devise measures to:
|
| High-quality online content | Involve the State in initiatives to develop high-quality and local online content, in order to attract a wide public audience |
| Support for industry | Take steps to support ICT businesses, as a way of stimulating the development of new and innovative services or products |
Governments and regulators clearly have a broad range of supply- and demand-side policy options that they can use to support the development of broadband – particularly high-speed broadband. It is important for governments to select the most relevant policies that reflect their own particular market situation and to assess each policy in terms of its potential impact and the difficulty of implementing it, as these factors vary considerably.
This article is based on a Working Paper prepared by Analysys Mason for the Broadband Commission, available for free at: http://www.broadbandcommission.org/Documents/publications/bb-Analysys-Mason-policy-briefing-paper-2015.pdf
Authors

Samer Mourad
Principal, expert in space and satelliteLatest Publications
Client project
Analysys Mason was engaged by the Welsh Government to assess and value the FibreSpeed network, and consider a range of options for its future
Client project
Supporting and advising on the governance and oversight of the EUR2.3 billion National Broadband Plan (NBP) network to ensure it delivers on the Irish government’s objectives to address rural broadband requirements
Article
Opportunities for network operators emerge as subsidy schemes enable rural broadband expansion

