Opportunities for network operators emerge as subsidy schemes enable rural broadband expansion
Network operators are well placed to take advantage of a growing number of government schemes around the world to extend broadband availability to rural populations. But these opportunities come with a caveat: bidding successfully for publicly-funded contracts requires specialist skills that commercial operators may not yet have developed. Without these, bids can run into difficulties and delays.
Analysys Mason has extensive experience of working with network operators to tender for government contracts and is in a prime position to help them navigate the complex journey from pre-tender preparation to contract fulfilment.
Governments around the world are responding to the need for broadband services in remote and rural areas with subsidy models that will be attractive to some network operators and their investors.
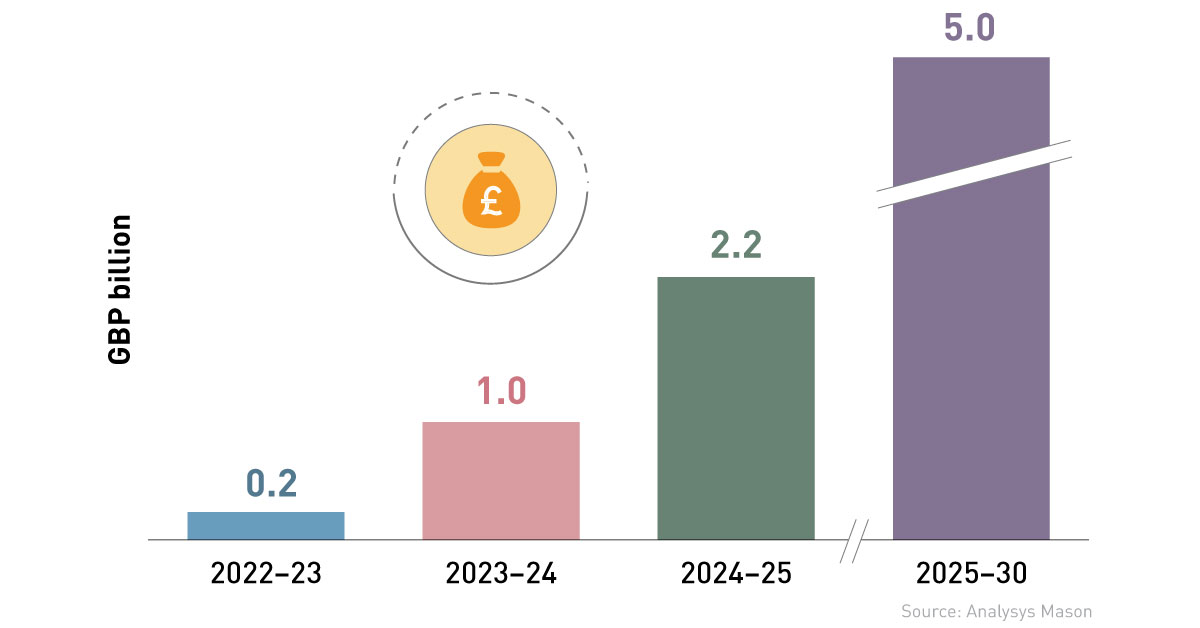
In the UK, the government’s Gigabit Infrastructure Subsidy scheme, launched in 2021, is well under way (Figure 1). Elsewhere, National Broadband Ireland is rolling out a fibre-to-the-premises (FTTP) network in rural Ireland, the country’s largest infrastructure project since rural electrification, while in Germany fibre roll-out is central to the government’s Digital and Gigabit Strategies.
Figure 1: Estimated cumulative allocation of Gigabit Infrastructure Subsidy funds
The US rural broadband market is also evolving fast. A number of Federal Government grants have been allocated to fuel broadband infrastructure development. Here, growth is also being driven by the penetration of FTTP into areas where ultrafast broadband has previously been dominated by cable networks. For example, AT&T has initiated its ‘Gigapower’ joint venture with Black Rock for FTTP. Despite an initially small roll-out, it has the potential to bring the benefits of FTTP and open access to the many areas of the country underserved by broadband infrastructure and connectivity.
Many countries have policy ambitions for extensive gigabit-capable broadband coverage, which presents opportunities for fibre network operators because government subsidy schemes will be needed to reach areas where broadband roll-out is not commercially viable.
Despite the differences between the many subsidy schemes in each country, they represent an opportunity for network operators to build scale and expand into new markets. With those opportunities, however, come considerable and unfamiliar challenges for operators seeking to meet the requirements of government contracting, which are very different to the commercial world they are used to. Analysys Mason’s experience in working with network operators bidding for contracts under the Gigabit Infrastructure Subsidy scheme has revealed skills gaps that can impede and affect the quality of bids throughout the bidding process. We have recently helped operators to bid successfully for five contracts in the UK. At the same time, our work with the Irish government developing tender documentation and supporting roll-out contract management for the National Broadband Plan has given us unique insight into the stringent governance under which public-funded subsidies are awarded.
The benefits of scrutiny
Preparing for the scrutiny to which bids are subjected on the long journey from the pre-tender stage to mobilisation and contract delivery is an intensive process that involves all aspects of an operator’s business. The agility required to change operational systems in order to meet such rigorous compliance rules can be daunting – and might even dissuade an operator from embarking on the process.
The challenges that must be navigated on this journey in order to meet the milestones are substantial. They begin at pre-tender stage, even before the bidding procedure has started, and potential pitfalls lie in wait at every stage along the way. For example, it is imperative to clarify the technical and commercial requirements necessary to comply with wholesale access obligations, as well as the financial requirements and penalties operators could face for non-compliance.
Beyond these complexities, the additional business benefits that accrue by pursuing the process can be significant. When operators answer the questions in the tender, they will also identify improvements that they can make to the way they operate, and extend their own business capabilities.
Coming from a commercial perspective, some network operators may be dissuaded by the daunting and granular preparation necessary to put such a bid together, but withdrawing could mean missing a significant opportunity for expansion.
One size does not fit all
Given the complexities of individual subsidy programmes, there is no single template to suit every case. But there will always be submission templates that can be reshaped for future contracts. Working with an expert who understands those complexities and also understands the time, effort and commitment required to tender and bid for government contracts is a good way to build the knowledge and skills network operators will need in order to take advantage of these significant new opportunities.
In its detailed overview of the Gigabit Infrastructure Subsidy, the UK government outlined the procurement procedure that bidders will be required to follow. They give an idea of the evidence and detailed responses operators will have to provide. This is just one example of such a subsidy, but regardless of the degree of localisation unique to individual contracts in the UK – a variation that will be magnified considerably in the complex emerging broadband landscape of the USA – there is likely to be a common core set of requirements at the heart of all similar projects. They will almost certainly include, for example, guarantees of availability, network access and coverage, capacity, and pricing; the ability to deliver a technology plan to meet certain specifications; and commitments to meet operational KPIs.
Demystifying subsidised procurement
With our global experience of working with governments and operators on subsidy schemes, Analysys Mason has acquired a wealth of knowledge about how schemes are designed and how bidders are evaluated. We have seen the impact that failure to adequately prepare responses can have on a timely and successful outcome. We have also seen that the process gives operators a new insight into their existing businesses that can improve the way they operate. The benefits of engagement with subsidy-based broadband network procurement processes are plentiful, regardless of the initial complexity and challenges of doing so.
Subsidy is often a new concept for network operators. We have seen how a lack of necessary skills can leave them exposed even at the earliest stages of engagement, which requires a keen focus on capability and capacity. We have also seen the effort needed and the delays that arise because the operator has provided inadequate documentation.
We want to work with operators to help them overcome these hurdles so they can take full advantage of the opportunities that bidding for publicly-funded contracts can bring. These opportunities will only grow in number as governments rise to their own challenges of extending vital rural broadband coverage.
For further details about how Analysys Mason can support bidding for, and delivering, government contracts for broadband subsidies, please contact Ian Adkins.
Article (PDF)
DownloadAuthor

Ian Adkins
Partner, expert in broadband and digital infrastructureRelated items
See moreArticle
Rural coverage initiatives: stakeholders can learn from the successes and failures of past efforts
Article
Rural broadband: making the right technology choice
Article
Rural broadband presents new opportunities and unique challenges for the telecoms industry

