AI: mitigating the cyber-security risks and considering its potential for businesses
The emergence of public large language models (LLMs) such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT has sparked an increase in conversations about artificial intelligence (AI) in public discourse. However, it is important to note that the AI sphere is not only made up of LLMs, such as ChatGPT, but that AI is an umbrella term that encompasses a variety of technologies that have the potential to reshape the everyday experience of individuals. Interest in AI extends beyond the public sphere, as regulatory bodies and companies have also begun to question its impact, importance and risks.
Despite the groundbreaking progress made in the past two years the AI field, it is still in its early stages, and only a limited number of technologies within this realm have managed to reach the anticipated potential that was widely predicted. Nevertheless, even at its current stage, AI has the potential to greatly increase enterprise productivity and pave the way for innovative business practices.
Although AI offers numerous advantages, it is important to consider the risks associated with its implementation. Companies are currently facing difficult decisions regarding AI implementation, particularly concerning security and compliance.
What challenges lie ahead?
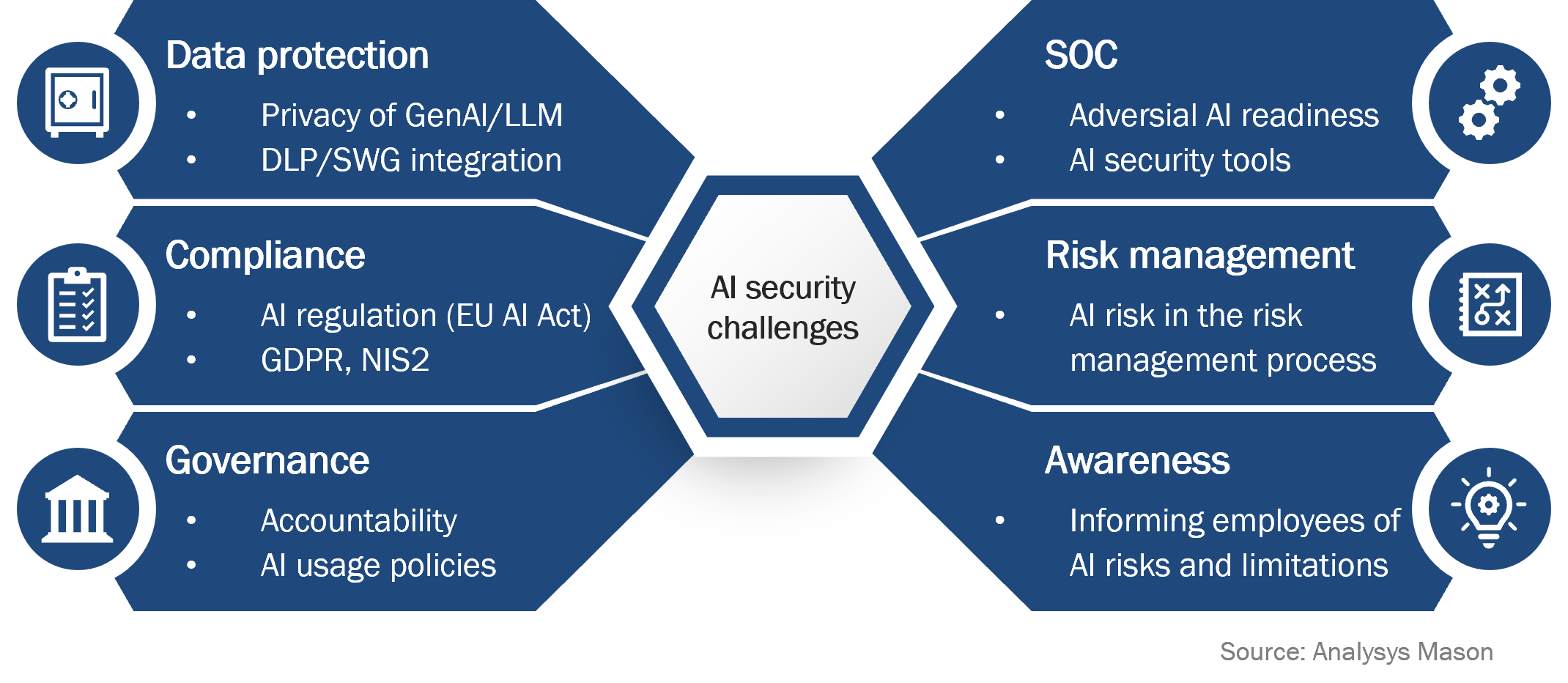
Companies can choose different approaches to AI. Those that actively reject AI are at a higher risk of falling behind their competition. On the other hand, companies that enable the use of AI systems with little to no guidance or security measures could face disastrous outcomes. This can lead to incidents that can cause great harm to the company or even endanger its existence. Those actively trying to implement AI are facing many challenges within a security context, such as:
- Data protection: Many publicly available LLMs such as ChatGPT have a permissive privacy policy and will store and leverage user input for further training of the AI model, potentially leading to public disclosure of sensitive corporate information. Even on-premises AI systems may be used in a manner that could lead to the disclosure of information to unauthorised personnel.
- Compliance: Given the novel nature of AI, many pieces of regulation specifically targeting AI systems – such as the EU AI Act – are yet to take effect. Even so, companies need to prepare in order to ensure adherence to these regulations and must consider the implications of existing regulatory frameworks such as the Network and Information Systems Directive 2 (NIS2) and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Governance: Companies lacking clear accountability and policies (for example, acceptable use policy), face distinct risks in the AI context. Public cloud-based LLMs encounter different challenges compared to on-premises LLMs, requiring tailored policies to address their unique threats.
- Security operations centre (SOC): Ensuring operational readiness of the SOC is key, given that the vast potential of AI is being leveraged not just by businesses, but also by potential intruders and hackers (adversarial AI). The SOC also needs to adapt in order to be prepared to use AI-supported cyber-security solutions which may generate large amounts of information.
- Risk management: The existing risk management process may not cover the full scope of AI-induced risk, such as the security of AI-generated code in software development. Companies must therefore adapt all elements of their risk management process to cover these threats.
- Awareness: Employees may not be aware of the security implications and limitations of AI systems. Companies must therefore proactively introduce trainings and ensure employee awareness of AI-related risks.
In essence, AI introduces new risks across all domains of cyber security and companies need to be aware of them. In Figure 1, we provide an overview of the various domains of cyber security, which are facing new challenges due to the emergence of AI.
Figure 1: AI cyber-security challenge dimensions
Enabling the potential of AI and mitigating the risks it poses
Given the novel nature of AI, regulatory requirements and common practices for a safe set-up are still in development, however, several formal guidelines have been published. The cyber-security frameworks published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) from the U.S. Department of Commerce are omnipresent throughout all domains of cyber security. Since 2023, NIST has been providing organisations with the AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF), a framework developed by NIST to help companies manage AI risks. The RMF targets the mapping, governance and management of AI-linked risks.
One essential component that businesses must consider when implementing AI is the characteristics of trustworthy AI systems as defined by NIST. The characteristics provide an approach that does not solely consider the IT security of AI systems, but also caters to other associated risks such as the bias and accountability of AI systems.
NIST’s AI RMF is just one possible approach for companies to consider when implementing new AI technologies. With the approaching implementation of the EU AI Act, many of the upcoming regulatory requirements for enterprises with a presence in the European Union (EU) may have to adhere to AI-relevant International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards such as ISO 23894 and ISO 42001. However, for businesses to be fully prepared for AI implementation, companies need to not only seek baseline compliance but also rethink and adapt all aspects of their cyber security frameworks, from awareness to security operations. Companies must also carefully integrate and adapt existing security solutions, such as secure web gateway (SWG), data loss prevention (DLP) security information and event management (SIEM) to address AI-related risks.
How can Analysys Mason support your business?
AI is not merely an increment of technological development, but a milestone and novel branch of technology which can enable new levels of productivity for your business. We at Analysys Mason believe that AI needs to be treated as transformational and we aim to support you and your business in a targeted manner. Our extensive track record of implementing successful cyber-security transformations enables us to help you leverage the full potential of AI while ensuring security and compliance. We begin by analysing your company’s specific regulatory, as well as internal, requirements and then develop and implement a comprehensive strategy and process for managing all AI-related security risks. As AI continues to reach new targets, we are here to make sure that your business is ready for the challenges ahead.
Article (PDF)
DownloadAuthor

Adam Salač
Senior ConsultantRelated items
Article
Five steps to fortify your supply-chain cyber-security resilience
Project experience
Securing the future with integrated IT operations
Project experience
Strengthening cyber-security governance and compliance at Sunrise

