AI’s Impact on Enterprise VSAT
AI (Artificial Intelligence) has become a reality, and it is looking to transform industries across various sectors. The satellite Industry is no exception as it encompasses a wide range of use cases, solutions, and competitors. Recently, Amazon announced Amazon Forecast that uses machine learning techniques to maximise satellite communication usage. NSR envisions more such solutions and further extension of these solutions will be needed to completely capture the benefits of technologies such as machine learning and AI. One of the key satellite industry segments that must embrace AI is Enterprise VSAT as it offers limited greenfield opportunities. As such, stakeholders must look for innovative ways to promote solution optimisation and thus promote a sustainable business.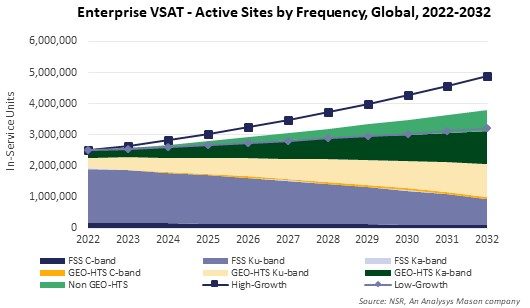
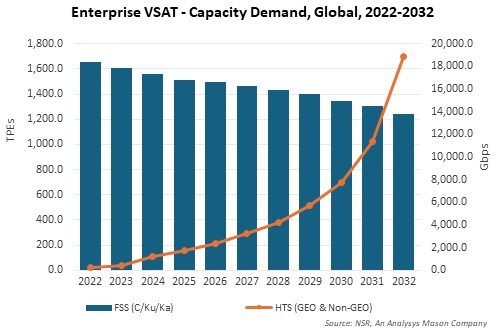
According to NSR’s Consumer and Enterprise Broadband via Satellite, 22nd edition report, Enterprise VSAT in-service units are projected to grow at a moderate CAGR 4.2% during 2022-2032. GEO-HTS and Non-GEO-HTS sites are projected to grow at an attractive pace, but the majority of this growth will be from user migration from FSS capacity to HTS capacity. Another major trend in the Enterprise VSAT market is that satellite capacity demand per site is growing at an encouraging rate as enterprises are investing in digital transformation and technologies such as AI, which has a cascading effect on bandwidth requirements. HTS capacity demand is forecasted to grow from 251 Gbps in 2022 to 18.9 Tbps in 2032 with Government/Military, Energy and Social Inclusion markets driving the majority of growth. But increase in capacity demand does not translate to increase in revenues proportionately, owing to aggressive competition and continued price erosion. Hence, stakeholders must iteratively look for innovation and technologies to remain most suitable in the ecosystem.
Why should the Enterprise VSAT market embrace AI?
The satellite industry, after years of innovation, is now able to make its assets and networks more and more flexible. This allows satellite operators and service providers to allocate required power & bandwidth over one beam or the other based on downstream demand, while the satellite is in orbit. Resonating with the times, AI has also become more real as it can handle massive volumes of data and take decisions accordingly. Additionally, the Enterprise VSAT segment covers a wide range of applications such as Retail, Hospitality, Banking, Energy – Oil & Gas, Energy – Mining, Energy – Utilities, Social Inclusion, Government/Military, and others with different bandwidth usage behaviour. AI integrated with Satcom flexible capabilities can lead to significant bandwidth & cost optimization opportunities and in the ongoing competitive ecosystem, this could be a game changer for a satellite operator or service provider.
One example where AI could play a role is in the battle between GEO-HTS and NGEO-HTS. The NGEO advantage of landing massive capacity to a site or multiple sites is largely due to the massive supply in NGEO that is and will blanket the earth compared to the supply being launched on GEO-HTS. A GEO satellite on a Software-defined platform can integrate AI to provision bandwidth or move bandwidth from sites at non-peak usage to sites that are entering peak use. On the mobility front and as illustrated by Amazon, asset utilization can be tracked in real time such as maritime vessels where beams can be configured to align with the vessel movement & density and adjust bandwidth allocation of beams to address traffic requirements where they are most needed. The same analogy and application can be applied to fixed Enterprise VSAT sites, i.e. beams or higher bandwidth can be allocated from non-peak sites to units on peak hours, thereby delivering the most efficient network utilizing data-driven AI technologies.
On the end user side, enterprises are closely looking into AI advancements to improve different aspects of their businesses such as resource allocation, supply chain management, predictive maintenance, security & safety, automation, and others. These will need seamless movement of data across different sites in the network, resulting in increased demand for connectivity players. The satellite industry must build its narrative across these ongoing and upcoming trends.
The Bottom Line
The integration of AI into the Enterprise VSAT market holds immense potential for the satellite industry. With AI's ability to handle vast amounts of data and make data-driven decisions, it aligns perfectly with the satellite industry's growing flexible capabilities. Industry stakeholders must invest to analyse the potential of AI capabilities and how they can harness benefits at the earliest. NSR suggests that instead of developing these capabilities in-house, Satcom players should identify a suitable AI technology partner. As an analogy, when the Enterprise VSAT market was looking into cloud adoption, Satcom players partnered with players such as Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM cloud, AWS, etc. One note on Amazon Forecast is that Kuiper is under the Amazon umbrella, which may pose concerns from incumbent players since Kuiper will be competing on the same markets soon. But this is another topic to be vetted on a future NSR Bottom Line piece.
In this evolving landscape, the satellite industry must align its strategies with these ongoing and upcoming trends to remain relevant and provide value to its customers. Embracing AI is not just an option, sooner and not later, it will become a necessity for the Enterprise VSAT market players to thrive and compete.
Author

