The pandemic has not led to many strategy changes for operators, but some aspects require a rethink
04 January 2021 | Research
Article | PDF (4 pages) | Fixed Services| Future Comms| Mobile Services| SME Services| Smart Devices| Fixed–Mobile Convergence| Video, Gaming and Entertainment| Enterprise Services
Listen to or download the associated podcast
An extended version of this article is available for subscribers here.
The telecoms industry has suffered limited damage as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic; revenue figures for most operators have fallen slightly, but few have encountered anything that is particularly severe or long-lasting. As a result, few operators have made significant changes to their strategy.
However, some aspects of the telecoms sector have been significantly affected by the pandemic. The most obvious is business services; revenue in this segment declined sharply for most operators in 2020 and prospects for 2021 are uncertain. Operators may have to rethink important parts of their strategies related to these aspects.
The telecoms industry has been affected by the pandemic in many different ways, and we have grouped these into three main categories (Figure 1). We will discuss each of these briefly, but will first look at the impact of the pandemic on operator financials in 2020.
Figure 1: Summary of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the telecoms industry
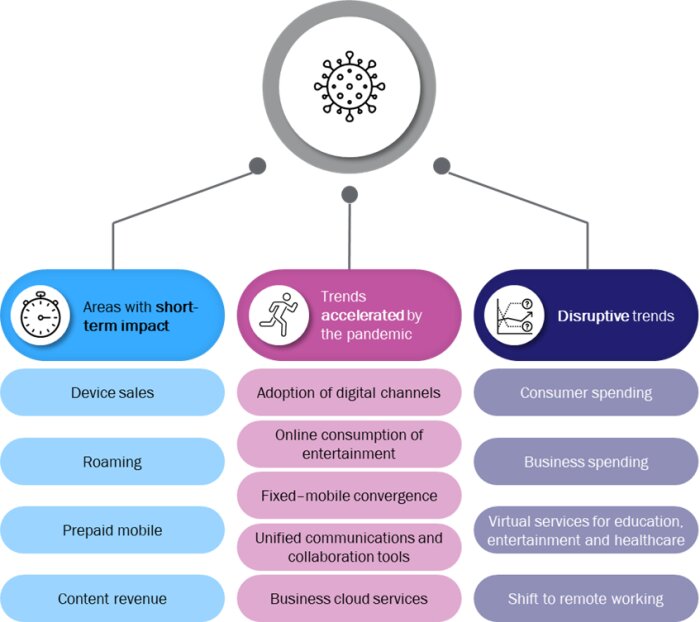
Source: Analysys Mason, 2021
Operators have outperformed their domestic economy in almost all countries
Operators’ financial performance during the first 9 months of 2020 was strong relative to the economy (Figure 2). Indeed, operators performed better than the broader economy in almost all cases and four of the nine operators in Figure 2 even grew their revenue in the last year (including MTN, despite the 17% decline in GDP in South Africa). The results relative to GDP are not especially surprising; the telecoms sector is typically resilient during a crisis, as we saw in 2008. This time around the sector has been even more critical in keeping the economy going.
Figure 2: GDP growth to 3Q 2020 and year-on-year domestic revenue growth of selected operators in 9M 2020
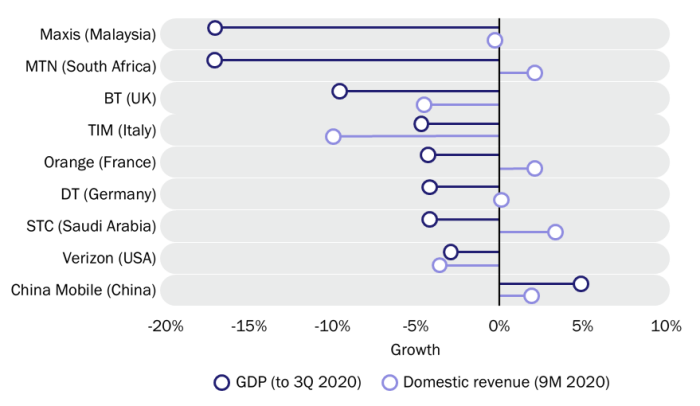
Source: Analysys Mason, 2021
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on operator profitability has been even more limited. The simple average of the EBITDA margins of the nine operators in Figure 2 in 2020 is almost identical to that in 2019.
Many areas were not hit by the pandemic or will bounce back once the pandemic is over
Many parts of the operator business have carried on much as before. Fixed broadband revenue, for example, has continued to grow steadily during the pandemic, driven mainly by ongoing fibre roll-outs. Other parts of the telecoms industry have suffered from the COVID-19 pandemic, but we expect that the impact will be short-lived. The aspects include:
- devices sales
- roaming
- prepaid mobile (in some countries at least)
- content revenue.
Revenue has been affected significantly in these areas, but it will recover, even if there is a period of readjustment in some cases.
Some existing trends accelerated during 2020
The trends in this category all existed before 2020, but they have accelerated in response to the pandemic Operators are well-placed to take advantage of these trends, but more effort may be required if they are to fully benefit. Aspects of the operator business that fit into this third category include the following.
- The adoption of digital channels. The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital channels. Operators will be keen to ‘lock in’ the behavioural changes of 2020 and continue to deliver cost savings through digital experience initiatives.
- The online consumption of entertainment. The shift towards the online consumption of entertainment content is likely to stay, and operators can do more to address this opportunity.
- Convergence. Convergence is not a new strategy, but the COVID-19 crisis has reinforced some of the benefits. For example, Deutsche Telekom said that “convergence is resilience” during the pandemic.
- Unified communications and collaboration tools for businesses. This is another area where usage has accelerated and operators are taking a reasonable share of the associated revenue growth.
- Business cloud services. Operators’ cloud revenue is growing quickly, but may not be scaling at the same rate as the market opportunity.
Some disruptive trends were initiated by the COVID-19 outbreak
Some disruptive trends have emerged due to the pandemic, and new opportunities will emerge from them. However, operators may struggle to respond; they may need to change their strategies or develop new initiatives to benefit from these changes, which include the following.
- The disruption to consumer spending trends. Consumer spending on telecoms has been largely unaffected by the pandemic, but operators may need to adapt their strategies to reflect uncertain economic conditions. Flexibility should be a guiding principle for operators. Customers may value a particular service and be willing to pay more for some extras, but do not want to commit on an on-going basis.
- The disruption to business spending trends. Business spending on telecoms is already feeling the effects of the pandemic, and the outlook is uncertain. This is a big change to the situation in 2019, when the overall outlook was positive.
- The adoption of new virtual services for entertainment, healthcare and education. It is now clear that many types of services can be delivered virtually. The new ways of interacting are likely to continue to some extent now that consumers have become comfortable with them.
- The shift to remote working by many organisations. The shift to working from home and the accelerated adoption of cloud services change the nature of the opportunity for operators. Pre-pandemic, the focus for many was on providing connectivity to business sites such as offices. This focus needs to change.
Operators’ existing assumptions now look outdated
The overall impact of the pandemic on operators has been relatively limited. Most have experienced slightly lower revenue growth and roughly flat profit margins. Much of their business has been unaffected. However, operators should not ignore the areas where the pandemic will have a more significant longer-term impact. Assumptions of a stable economy and a continuation of existing service and technology trends often underpin an operator’s strategic plan. For some of the services offered by operators, business services in particular, these assumptions look outdated and may need a rethink.
Article (PDF)
Download
Insights into how COVID-19 will impact the TMT industry and how to navigate the challenges
Authors

Tom Rebbeck
Partner, expert in TMT consumer and business servicesRelated items
Survey report
How home Wi-Fi affects broadband user experience: consumer survey
Article
AT&T will focus on mobility, fibre and FMC to drive growth in the consumer and business segments
Survey report
Streaming video opportunities for operators: consumer survey

